the Launch of IEA Report Gas 2021 Analysis and Forecast to 2024
On July 8, the International Energy Agency's Natural Gas Analysis and Outlook 2021-2024 report was released in Beijing. The launch was jointly organized by the IEA, Peking University Energy Research Institute, the China-U.S. Energy Cooperation Program, and the Shanghai Oil and Gas Trading Center. More than 100 guests, including officials from the National Energy Administration, national pipeline companies, embassies and consulates of some countries in China, and experts from Chinese and foreign energy companies and media, gathered to discuss the direction of natural gas development, while about 50,000 people watched the launch online. Mr. Jean-Baptiste Dubreuil, Senior Gas Analyst from the International Energy Agency and Mr. Akos Losz, Gas Energy Analyst, gave a detailed interpretation of the report.

Natural gas demand to keep growing slowly, expected to reach 4.3 trillion cubic meters in 2024, up 7% from before the epidemic
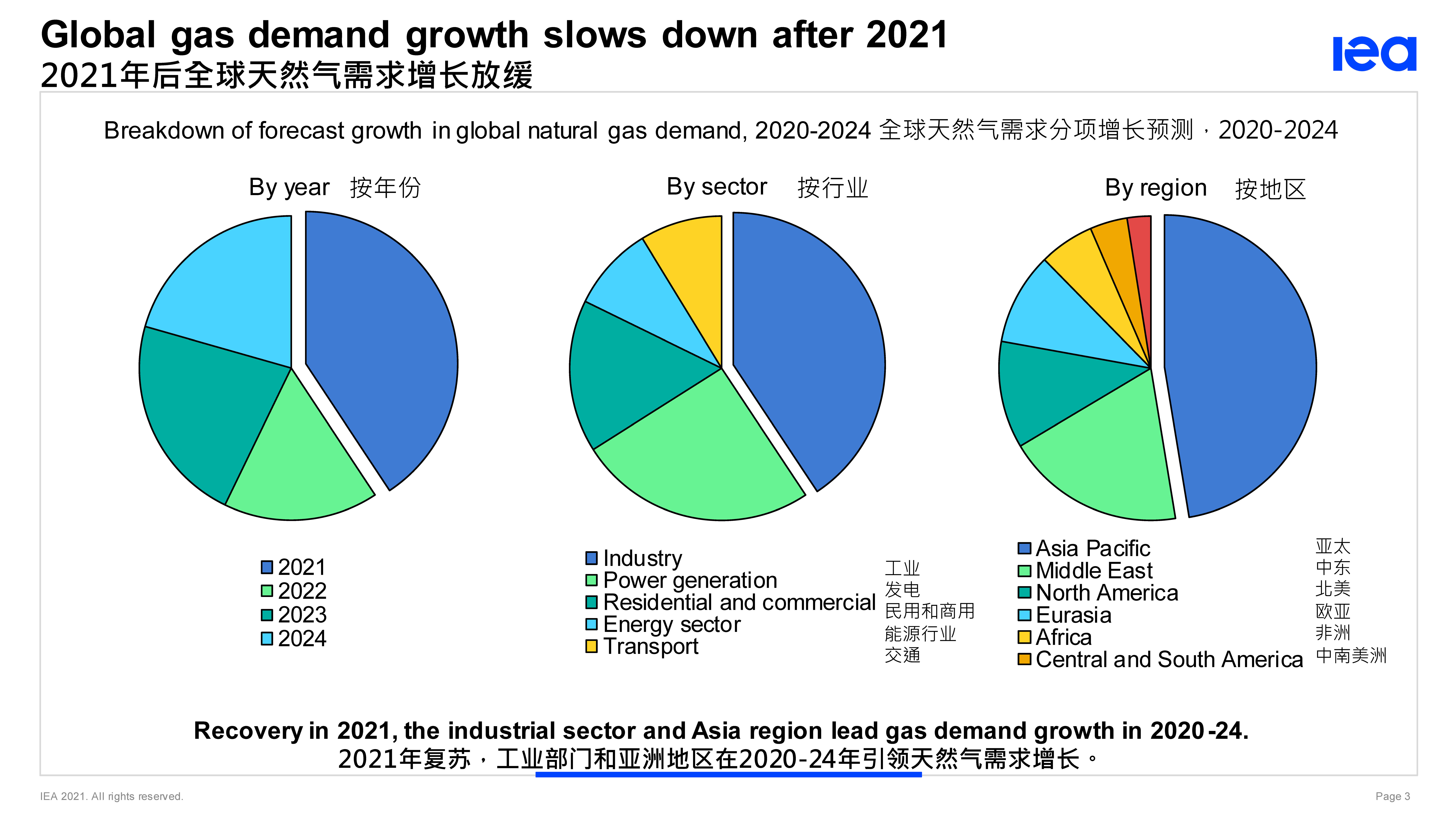
The report notes that global natural gas demand fell 1.9 percent, or 75 bcm, over the past year due to the economic downturn caused by an unusually warm winter in the Northern Hemisphere and the New Crown pneumonia pandemic. The main declines occurred in mature markets such as North America, Eurasia and Europe. Global gas demand is expected to rebound by 3.6% in 2021, fully recovering to pre-2020 levels. While gas reductions will not fully match declines in some mature markets, there is net growth in Asia Pacific, Africa and the Middle East, driven by a recovery in economic activity.
Looking ahead, natural gas will continue to grow at a slow pace over the period 2021-2024. By 2024, natural gas demand is expected to approach 4,300 bcm, an increase of 350 bcm, or 9%, compared to the low point in 2020. Natural gas will recover rapidly in the short term, and then the growth rate will slow. Demand growth in 2021 is expected to account for about 40% of total growth from 2021-2024. Global natural gas consumption grows at a rate of 3.6% in 2021, then gradually declines in subsequent years to 1.7% in 2024. Compared to 2019, natural gas increases by only 275 bcm, or about 7%, over the forecast period. Growth will be driven primarily by natural gas demand in the industrial sector. Growing demand for natural gas due to industrial gas and natural gas to fertilizer is expected to account for 40% of the total gas consumption growth in 2020-2024. Asia Pacific, i.e. China, India and the Emerging Asia region, will account for nearly half of the gas growth.
2050 Net Zero Pathway Needs Stronger Policies
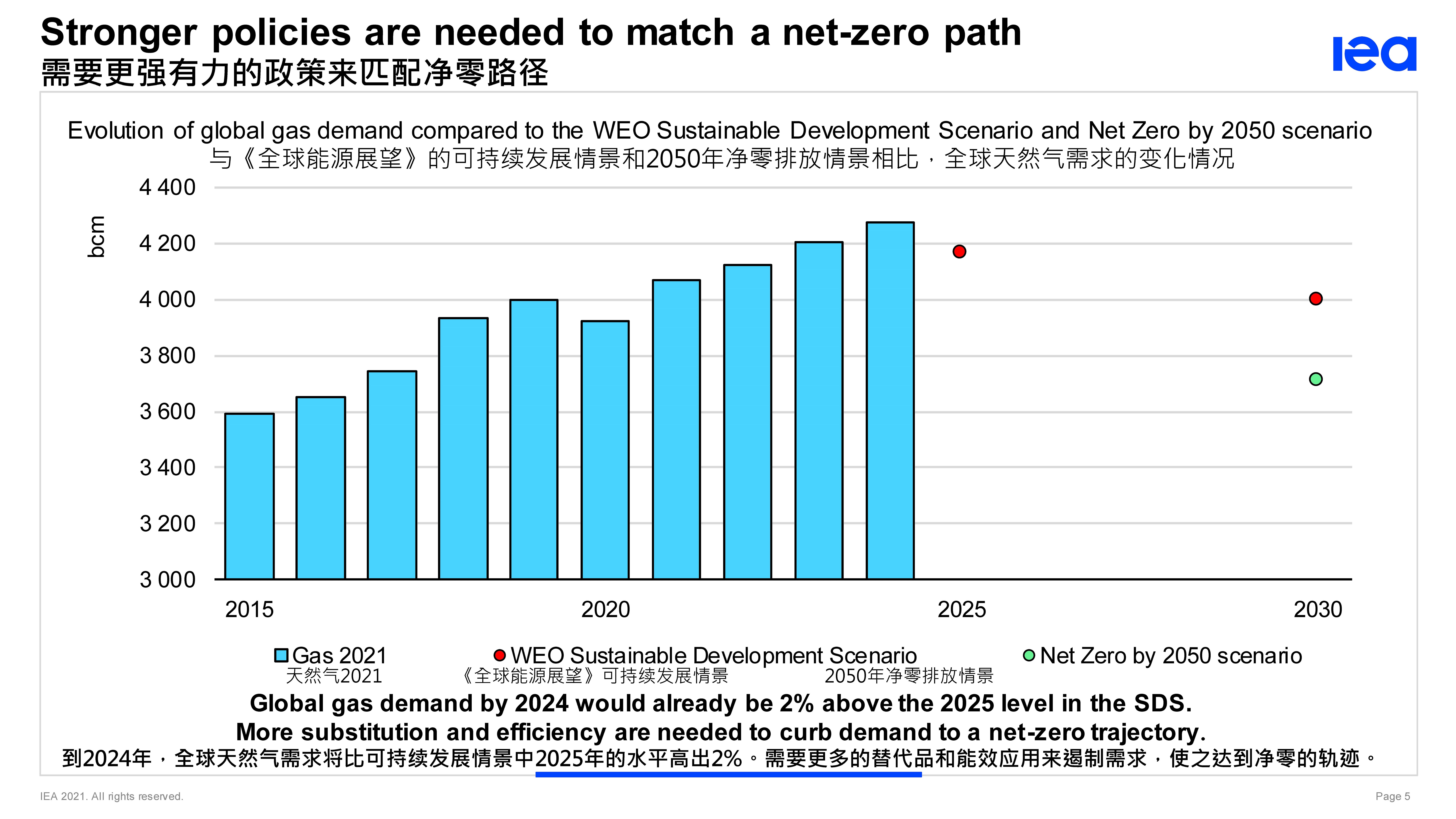
Global gas demand growth over 2021-2024 is driven in both directions by economic activity and fuel substitution. Over the forecast period, the substitution of coal and petroleum products with natural gas results in an increase in natural gas demand of approximately 160 bcm. The growth in global natural gas demand over the 2020-2024 period, while relatively modest, is still relatively high compared to the forecast period (2021-2025) indicated in the Net Zero 2050 - Global Energy Sector Roadmap of only 4%. However, the growth of only 4% over the forecast period (2021-2025) indicated in the "2050 Net Zero - Global Energy Sector Roadmap" is still high and is not consistent with achieving the goal of net zero emissions by 2050. "To achieve the emissions pathway set out in the roadmap, stronger policies will need to be introduced over our forecast period to support further fuel substitution and efficiency gains," The report said. The gas industry needs to take a range of measures to reduce the intensity of greenhouse gas emissions across the value chain and reduce pollution from natural gas flaring through carbon management programs. Of course, reducing such emissions is very time-consuming and costly. The IEA's Methane Tracker project concluded that a 40 percent reduction is cost-neutral, and that other synthetic methane, hydrogen and biomethane, which are more expensive to develop, will take some time.
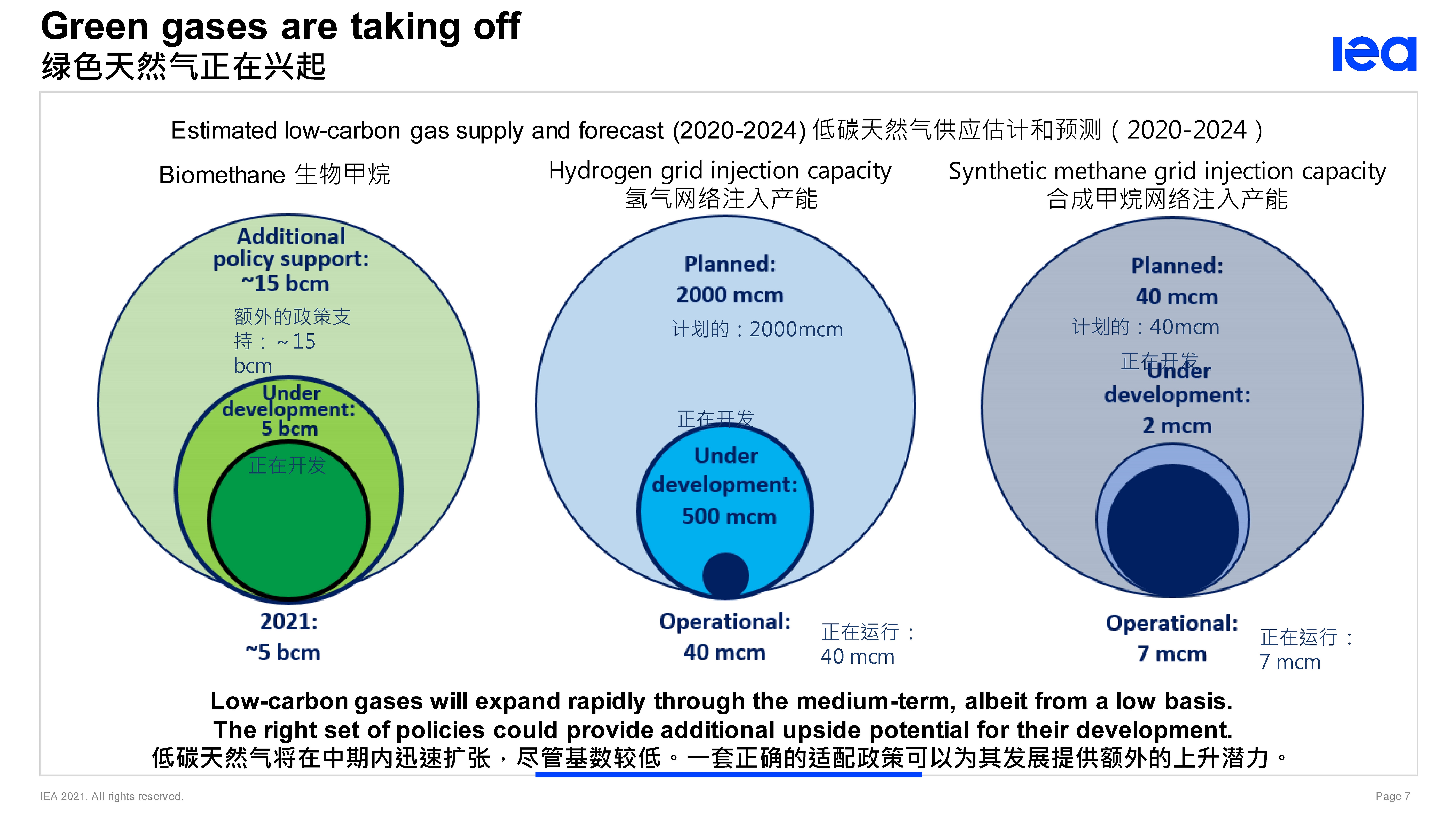
LNG market tightens, expected to return to pre-epidemic liquefaction utilization rates in 2024
In the LNG market, global LNG trade grows by 3% from 2020 to 2024, with the majority coming from Asia, particularly China, which is very likely to overtake Japan as the world's largest LNG importer. The report finds that China accounts for about 40% of the growth in global transportation demand. LNG investment decisions (FIDs) have been very volatile in recent years, and after a peak in investment in 2018-2019 and a complete stagnation due to the epidemic, there will be a further wave of investment in 2021 due to a strong economic recovery. "Global LNG utilization is expected to gradually return to pre-2020 levels by 2024. In the absence of major project delays or unplanned disruptions, the risk of a tight market structure through 2024 appears limited, with the possible exception of short-term seasonal events." The report notes.

